System Disk Utility 2.6.2 for Mac OS X Server 1.2 is a Mac OS program that allows you to select which hard disk your computer will start up from. To startup your computer with Mac OS X Server 1.2. Disk Drill: The best data recovery software for Mac OS X. Recover deleted or lost data from any storage device, iOS and Android.
Disk Utility User Guide
You can use Disk Utility to create a disk image, which is a file that contains other files and folders.
Note: You can burn information to a CD or DVD using the Burn command in the Finder. See Burn CDs and DVDs.
Create a blank disk image for storage
You can create an empty disk image, add data to it, then use it to create disks, CDs, or DVDs.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, choose File > New Image > Blank Image.
Enter a filename for the disk image, add tags if necessary, then choose where to save it.
This is the name that appears in the Finder, where you save the disk image file before opening it.
In the Name field, enter the name for the disk image.
This is the name that appears on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar, after you open the disk image.
In the Size field, enter a size for the disk image.
Click the Format pop-up menu, then choose the format for the disk:
If the disk image will be used with a Mac that has a solid state drive (SSD) and uses macOS 10.13 or later, choose APFS or APFS (Case-sensitive).
If the disk image will be used with a Mac with macOS 10.12 or earlier, choose Mac OS Extended (Journaled) or Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled).
If the disk image will be used with a Mac or Windows computer and is 32 GB or less, choose MS-DOS (FAT); if it's over 32 GB, choose ExFAT.
To encrypt the disk image, click the Encryption pop-up menu, then choose an encryption option.
Click the Partitions pop-up menu, then choose a partition layout.
Click the Image Format pop-up menu, then choose an option:
Sparse bundle disk image: Same as a sparse disk image (below), but the directory data for the image is stored differently. Uses the .sparsebundle file extension.
Sparse disk image: Creates an expandable file that shrinks and grows as needed. No additional space is used. Uses the .sparseimage file extension.
Read/write disk image: Allows you to add files to the disk image after it's created. Uses the .dmg file extension.
DVD/CD master: Changes the size of the image to 177 MB (CD 8 cm). Uses the .cdr file extension.
Click Save, then click Done.
Disk Utility creates the disk image file where you saved it in the Finder and mounts its disk icon on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar.
In the Finder, copy your files to the mounted disk image, then eject it.
Restore the disk image to a disk.
For more information about disk image types, see the manual (man) page for hdiutil.
Create a disk image from a disk or connected device
What programming language does excel use. You can create a disk image that includes the data and free space on a physical disk or connected device, such as a USB device. For example, if a USB device or volume is 80 GB with 10 GB of data, the disk image will be 80 GB in size and include data and free space. You can then restore that disk image to another volume.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, select a disk, volume, or connected device in the sidebar.
Choose File > New Image, then choose 'Image from [device name].'
Enter a filename for the disk image, add tags if necessary, then choose where to save it.
This is the name that appears in the Finder, where you save the disk image file before opening it.
Click the Format pop-up menu, then choose an option:
Read-only: The disk image can't be written to, and is quicker to create and open.
Compressed: Compresses data, so the disk image is smaller than the original data. The disk image is read-only.
Read/write: Allows you to add files to the disk image after it's created.
DVD/CD master: Can be used with third-party apps. It includes a copy of all sectors of the disk image, whether they're used or not. When you use a master disk image to create other DVDs or CDs, all data is copied exactly.
To encrypt the disk image, click the Encryption pop-up menu, then choose an encryption option.
Click Save, then click Done.
Disk Utility creates the disk image file where you saved it in the Finder and mounts its disk icon on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar.
Important: Don't create a disk image of a disk that you believe to be failing or that contains corrupted information. The disk image may not serve as a reliable backup.
For technical information about creating a restore disk image, see the Apple Software Restore (ASR) manual (man) page.
Create a disk image from a folder or connected device
You can create a disk image that contains the contents of a folder or connected device, such as a USB device. This method doesn't copy a device's free space to the disk image. For example, if a USB device or volume is 80 GB with 10 GB of data, the disk image will be 10 GB in size and include only data, not free space. You can then restore that disk image to another volume.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, choose File > New Image, then choose Image from Folder.
Select the folder or connected device in the dialog that appears, then click Open.
Enter a filename for the disk image, add tags if necessary, then choose where to save it.
This is the name that appears in the Finder, where you save the disk image file before opening it.
To encrypt the disk image, click the Encryption pop-up menu, then choose an encryption option.
Click the Image Format pop-up menu, then choose an option:
Read-only: The disk image can't be written to, and is quicker to create and open.
Compressed: Compresses data, so the disk image is smaller than the original data. The disk image is read-only.
Read/write: Allows you to add files to the disk image after it's created.
DVD/CD master: Can be used with third-party apps. It includes a copy of all sectors of the disk image, whether they're used or not. When you use a master disk image to create other DVDs or CDs, all data is copied exactly.
Hybrid image (HFS+/ISO/UDF): This disk image is a combination of disk image formats and can be used with different file system standards, such as HFS, ISO, and UDF.
Click Save, then click Done.
Disk Utility creates the disk image file where you saved it in the Finder and mounts its disk icon on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar.
For technical information about creating a restore disk image, see the Apple Software Restore (ASR) manual (man) page.
Create a secure disk image
If you have confidential documents that you don't want others to see without your permission, you can put them in an encrypted disk image.
Note: If you want to protect the contents of the system disk, turn on FileVault using the FileVault pane of Security & Privacy Preferences.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, choose File > New Image > Blank Image.
Enter a filename for the disk image, add tags if necessary, then choose where to save it.
This is the name that appears in the Finder, where you save the disk image file before opening it.
In the Name field, enter the name for the disk image.
This is the name that appears on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar, after you open the disk image.
In the Size field, enter a size for the disk image.
Click the Format pop-up menu, then choose a format:
If you're using the encrypted disk image with a Mac computer using macOS 10.13 or later, choose APFS or APFS (Case-sensitive).
If you're using the encrypted disk image with a Mac computer using macOS 10.12 or earlier, choose Mac OS Extended (Journaled) or Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled).
Click the Encryption pop-up menu, then choose an encryption option.
Enter and re-enter a password to unlock the disk image, then click Choose.
WARNING: If you forget this password, you won't be able to open the disk image and view any of the files.
Use the default settings for the rest of the options:
Click the Partitions pop-up menu, then choose Single partition - GUID Partition Map.
Click the Image Format pop-up menu, then choose 'read/write' disk image.
Click Save, then click Done.
Disk Utility creates the disk image file where you saved it in the Finder and mounts its disk icon on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar.
In the Finder , Open it zip. copy the documents you want to protect to the disk image.
If you want to erase the original documents so they can't be recovered, drag them to the Trash, then choose Finder > Empty Trash.
When you're finished using the documents on the secure disk image, be sure to eject the disk image. As long as it's available on your desktop, anyone with access to your computer can use the documents on it.
To access the data in a disk image, double-click it. It appears on your desktop, and you can add, remove, and edit files on it just as you would with a disk.
Dec 16, 2020 • Filed to: Solve Mac Problems • Proven solutions

Do you know that mini heart attack you get when your Mac crashes or would not start? It is the worst feeling in the world, especially if you have a lifetime worth of work stored inside your machine. What should you do in these situations? As you are probably have been advised many times, backing up your data regularly is a great practice. For Mac users, setting up an OS X Recovery Disk would be beneficial when trouble strikes. For example, it is conducive to Mac file recovery while you find data lost.
What Is an OS X Recovery Disk?
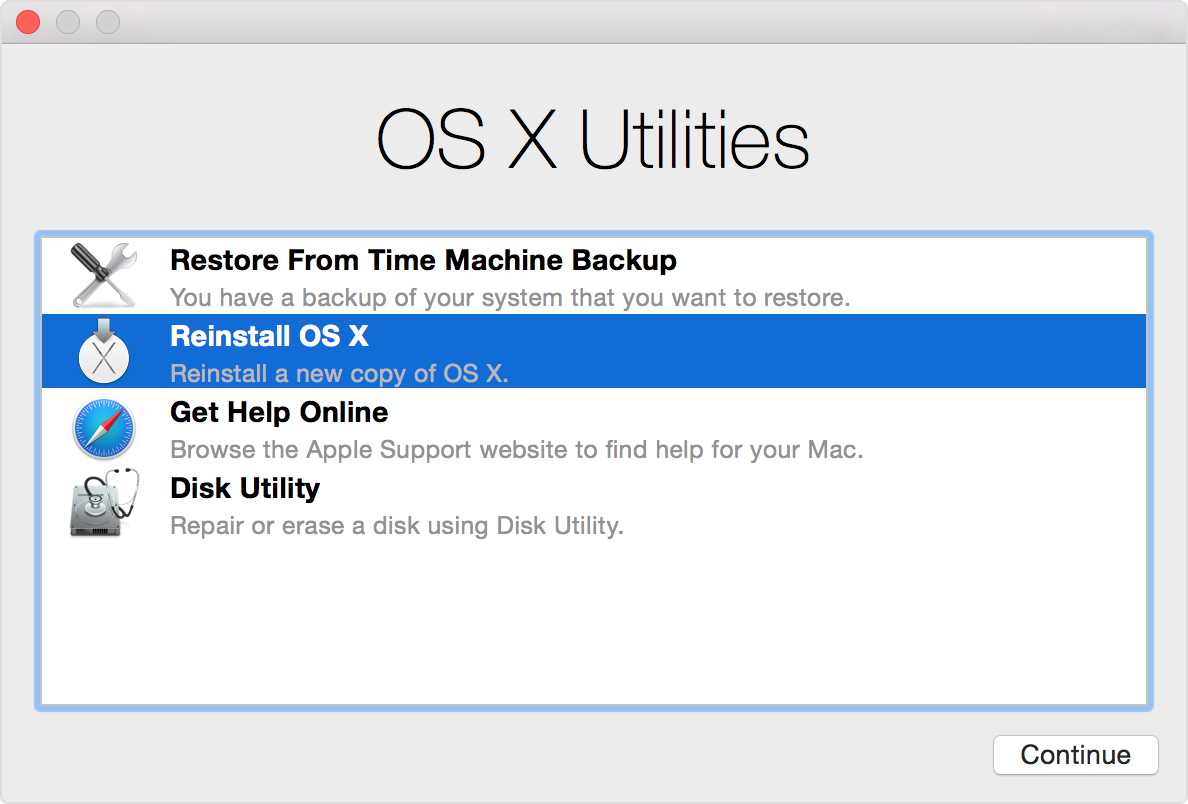
The OS X Recovery Disk is a native but hidden recovery volume on your Mac hard drive. This feature can be used to start up your machine and perform emergency maintenance services such as repairing a corrupted drive by running Disk Utility, surf the Internet to assess the problem you might be experiencing or download any necessary updates. You can also use the OS X Recovery Disk to reinstall your operating system and restore lost data from Time Machine backup.
Part 1 How to Restore Mac with Recovery Disk Mac
Now that you know that your machine has a built-in recovery tool, you may ask, 'How to use the OS X Recovery Disk?' The feature allows you to do the following options:
- Use Time Machine backup to restore your Mac.
- Reinstall Mac OS X with a recovery disk.
- Get help online or check your internet connection.
- Use Disk Utility to verify and repair connected disks.
Here is how to repair Mac disk and recover Mac with OS X Recovery Disk:
- To put your Mac into Recovery Mode, restart your machine and hold down the 'Command + R' keys on your keyboard simultaneously. Continue to do this until the Apple logo appears.
- When your Mac has started up, the OS X utility window will appear and prompt you to choose one of the four options listed above. (Note: if you do not see this, but instead see a login page, you will need to restart your Mac and do the whole process again).
- Click 'Disk Utility' and choose the drive you want to repair on your Mac. Open the 'First Aid' tab. To check the problem your Mac has, click the 'Verify Disk' button. Click the 'Repair Disk' button to start fixing this button.
Part 2 How to Create an OS X Recovery Disk
Since OS X Mountain Lion, everything went digital and maintenance-minded. Mac users could no longer depend on physical recovery disks to help them fix any problems on their machines. But what how can you access this hidden partition if something goes wrong with your hard drive? You can always connect your computer online and initiate the OS X Internet Recovery feature, but realistically, you may not always have an internet connection. This method will also not work if you had upgraded an old Mac to run on a newer version of OS X.
In these situations, having your OS X Recovery Disk easily accessible on an external USB drive or SD card would be beneficial. It is straightforward. Read on to learn how to create OS X Recovery Disk that you can easily access anywhere, anytime. Before you start, here are some of the things you need to adhere to:
- To create an OS X Recovery Disk, make sure that your machine is at least running on OS X Lion or Mountain Lion and that there is an existing Recovery System on its startup volume. If you have a newer Mac, use Internet Recovery to get the system online.
- An external USB drive or SD card with at least 1GB free space.
Once you have made sure both requirements are fulfilled, follow the following steps to create an OS X recovery disk:
- Download the Recovery Disk Assistant from the Apple website if you do not have it already in your Applications/Utility folder.
- Wait until the download is complete and double-click on the file, which should be named 'RecoveryDiskAssistant.dmg.' This will create the Recovery Disk Assistant.appfile - drag it into your Applications folder.
- Attach an external hard drive or USB stick and launch the Recovery Disk Assistant. Agree to the terms and conditions and wait until the software detects your external drive.
- Select the drive you want to use to create the OS X Recovery Disk. Click 'Continue'. (Note: all data in the selected drive will be overwritten so that the wizard can install the needed data to make the external hard drive or USB stick into a recovery disk.)
It will take some time for the process to complete. When the software prompts you that it is done, click on the 'Quit' button. Eject the new recovery disk and keep it in a safe place. You will be able to use the disk when you need it the most. It is also a good idea to update this disk regularly.
Part 3 How to Recover Data on Mac Hard Drive
How do I recover files on my Mac for free?
If you just want to recover deleted or lost files from Mac hard drive, you can rely on a free data recovery program to help you do that. For example, Recoverit Free Mac Data Recovery. This file recovery freeware for Mac is dedicated to recovering data on Windows or Mac computer. If you want to retrieve data from an external device, like an external disk or memory card, connect it to your computer and the stored data can also be recovered.
Recoverit - The Free Software for Mac OS Recovery
- Recover documents, photos, videos, emails, and more from Mac hard drive.
- Recover 1000+ types and formats of files in different data loss situations.
- Scan and preview the files before you recover them from all storage devices.
Video Tutorial on Windows and Mac Hard Drive Recovery
This free hard drive data recovery software is easy to use and user-friendly. Watch the video, and you can get three simple steps to recover your data from the hard drive.
3 Steps to Recover Files from Mac Hard Disk
Download Recoverit Free Data Recovery and take the next three steps to recover Mac hard drive data for free right away.
Select the recovery disk
To recover data from a Mac hard disk, please select the hard drive where you want to restore Mac data. Click the 'Start' button to move forward.
Open Disk Utility
Scan the Mac recovery disk
Recoverit Mac Disk Recovery will start an instant and all-around scan on the recovery disk. All the lost, inaccessible or deleted files on Mac will be shown gradually.
Preview and recover data
Once the scan ends, all the scanned files will be listed according to the file formats. You can preview the files, select the wanted ones, and click 'Recover' to get them back.
Having a built-in recovery solution is excellent, especially when you tend to lose or misplaced recovery disks. It would be great to learn how to use it and have a copy of it stored outside the machine so that you will be able to access it when you cannot do it straight from your computer. Fail to do it? Only want to recover data? Recoverit can help you. Download it and recover lost files for free.
What's Wrong with Mac
Mac Os X Disk Utility Restore
- Recover Your Mac
- Fix Your Mac
- Delete Your Mac
- Learn Mac Hacks
